
Share Important Moment of MileCell Bio with You
2024.09.13
Primary plateable hepatocyte culture is an important model for in vitro studies in drug development, including hepatotoxicity, drug transport, hepatitis virus infection, hepatic drug metabolism and hepatobiliary excretion.
Bile Canaliculi Staining
Confluent plateable transporter-qualified cryopreserved hepatocytes using Matrigel overlay promote the formation of biliary canaliculi. This format provides an in vivo-like model for studying biliary efflux and uptake drug transporters.
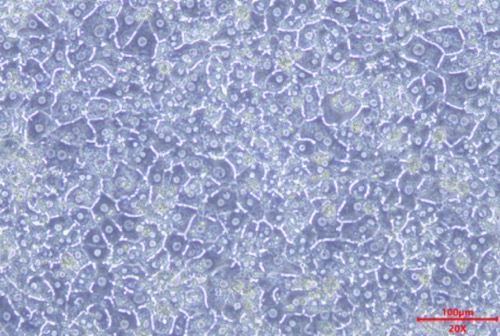
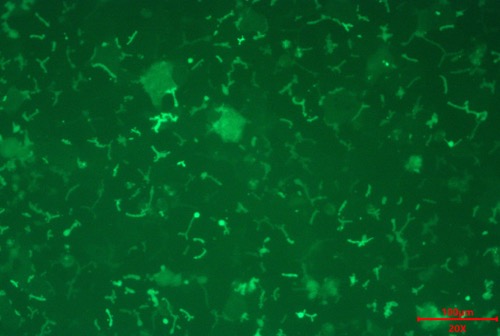
A:Day 3 Bright field B:Day 3 CDFDA
MileCell Bio cryopreserved SD Rat hepatocytes demonstrates 100% confluency (A) and forms bile canalicili (B) on day 3 in Collagen I substratum with Matrigel overlay culture. Fig B reveal the staining of CDFDA Uptake into Bile Canaliculi.
ASGPR Immunofluorescence Staining
Targeted delivery of Oligonucleotides to liver hepatocytes using N-acetylgalactosamine (GalNAc) conjugates that bind to the asialoglycoprotein receptor(ASGPRs) has become a breakthrough approach in the therapeutic oligonucleotide field. GalNAc is a highly specific ligand for ASGPR, which is predominantly expressed on the surface of hepatocytes.
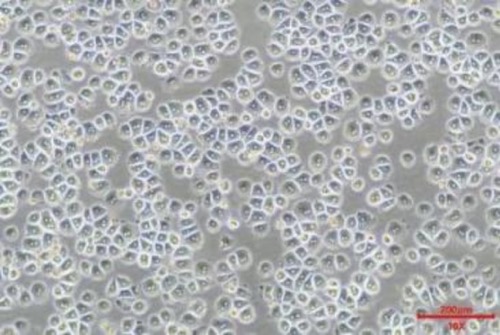
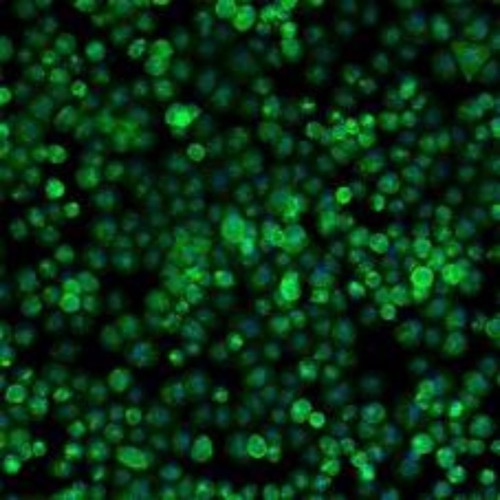
A.4h adhesion in Bright field(100x) B.Stained after 4h adhesion
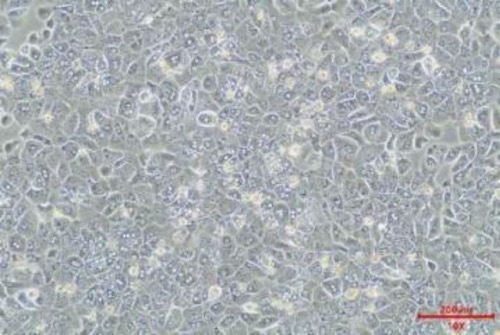
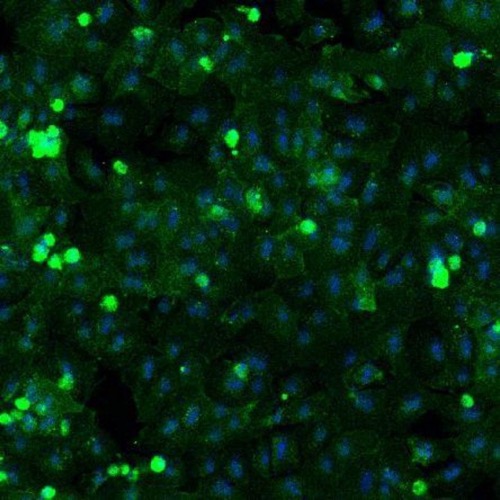
B. 24h adhesion in Bright field(100x) D.Stained after 24h adhesion
The expression of ASGPR decreased with the extension of hepatocyte culture. MileCell Bio cryopreserved Cynomolgus Monkey are adherent 4h(A&B) after resuscitation which meets the requirement of in vitro study of oligonucleic acid.
